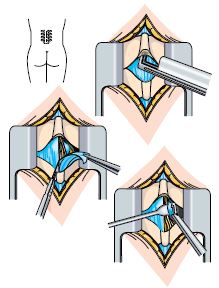
What happens during surgery?
Your surgery will take place in an operating theatre, where you will be put to sleep by an anaesthetist. In the operating theatre you lie on your front, over an arched operating table. The surgeon makes an incision, usually about 3-5 cm long, down the centre of your back.
|
|
Discectomy
A small amount of bone and ligament from the back of the spine are removed so the disc and nerve can be seen; this will not make your spine weaker. The part of the nucleus pressing on the nerve is trimmed.
Once the surgical procedure is completed the incision is closed with either stiches or clips, and a sterile bandaged applied.
Decompression
A small section of bone and ligament from the back of the spine are removed so the nerves have more space. This is called a laminectomy and will not make your spine weaker. The surgeon may also remove the osteophytes, this is called a foraminotomy.
Once the surgical procedure is completed the incision is closed with either stiches or clips, and a sterile bandaged applied.
|
|
Expectations of surgery
After surgery, there is a 65 to 90% chance of your leg pain reducing or disappearing altogether. A 25 to 50% chance that you will have back pain that may get worse. However, we hope that your pain will be reduced enough for you to be able to move about well enough to continue with your life, work and social activities.
Possible complications following spinal surgery
• Disc-space infection - this is an infection in the disc that was operated on. It is uncommon and is treated with antibiotics.
• Nerve damage - this is damage to the nerves in your back which can lead to foot drop (when you drag your foot while walking), altered feelings which can include pins and needles, temperature changes or no feelings in your back or legs (or both).
|
|
• Bleeding or haematoma (collection of blood).
• Bladder and or bowel problems - this may lead to incontinence (loss of control), which may be temporary or permanent.
• Dural tears or leaks – this is when the membrane covering the spinal cord (the dura) is damaged. This may lead to nausea, vomiting and headaches. It is usually treated with bed rest.
|